The Science of Coffee Roasting: How Temperature, Time, and Technique Shape Your Morning Cup
In the world of coffee, there's more than meets the eye (or should we say, taste buds). Behind that invigorating boost of caffeine lies a fascinating journey of science and art known as coffee roasting. The process of turning green coffee beans into the aromatic, flavourful beans we grind for our morning cuppa is a delicate dance of temperature, time, and technique.
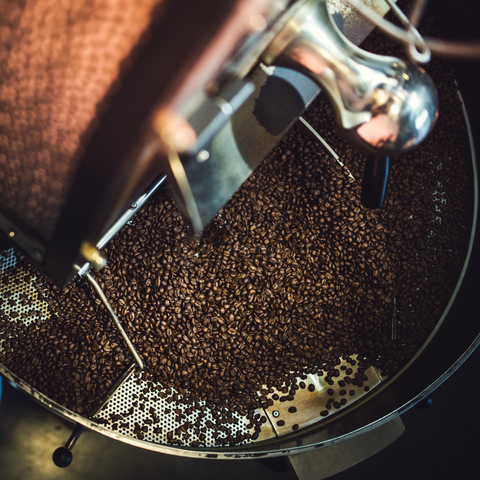

From the moment the beans hit the hot roasting drum, a symphony of chemical reactions takes place, transforming the raw material into a complex beverage that uplifts our senses. The key players in this roast-driven symphony are temperature and time, which work in tandem to unlock the beans' true potential. The roasting technique employed – whether it's the traditional drum roasting or the newer air roasting method – further influences the flavour profile, creating a unique experience with every sip.
So, if you've ever wondered why your favourite brew tastes the way it does, join us as we delve into the fascinating world of coffee roasting. We'll uncover the secrets behind temperature, time, and technique, and explore how they shape the beloved beverage that kickstarts our day. Get ready for a journey behind the scenes of your morning cuppa!
The importance of temperature in coffee roasting
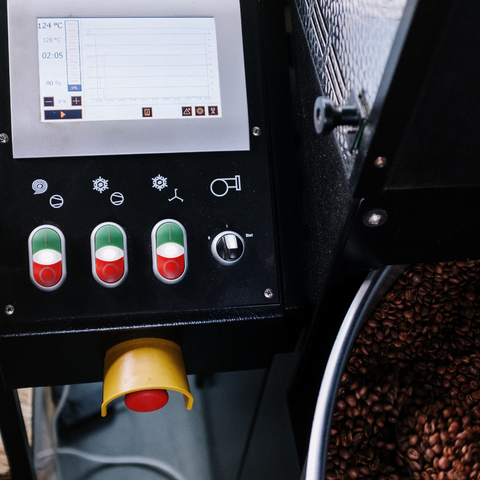

Temperature plays a pivotal role in coffee roasting, as it directly affects the chemical reactions that occur within the beans. When green coffee beans are exposed to heat, a series of complex reactions begin. The first stage is known as the drying phase, where the moisture within the beans evaporates. This is followed by the browning phase, where the beans undergo a series of chemical changes that give them their characteristic color and flavour.
During the drying phase, the temperature needs to be carefully controlled to ensure even moisture removal without causing the beans to scorch. Too high a temperature can result in an uneven roast and a burnt taste. On the other hand, too low a temperature can result in underdeveloped flavours.
As the browning phase begins, the temperature needs to be gradually increased to facilitate the Maillard reaction, which is responsible for the development of the rich, complex flavours we associate with a well-roasted coffee. The Maillard reaction is a chemical process that occurs between amino acids and sugars, resulting in the formation of hundreds of different flavour compounds.
To achieve the perfect roast, coffee roasters carefully monitor the temperature profiles throughout the roasting process, making adjustments as needed to bring out the desired flavours and aromas. It's a delicate balance between heat and time, with temperature acting as the guiding force.
Understanding the role of time in coffee roasting
Just as temperature is crucial, time also plays a vital role in coffee roasting. The duration of the roast has a direct impact on the flavour profile of the final product.

During the early stages of roasting, the beans undergo a process called pyrolysis, where the chemical composition of the beans changes due to the heat. This process releases volatile compounds, such as carbon dioxide, which contribute to the aroma and flavour of the coffee.
The length of the roast determines the degree to which these volatile compounds are released. A shorter roast will result in a brighter, more acidic cup, while a longer roast can produce a darker, fuller-bodied brew. The timing also affects the level of caffeine in the coffee, with lighter roasts generally containing higher caffeine content than darker roasts.
Coffee roasters carefully track the time during the roasting process, adjusting it as necessary to achieve the desired flavour profile. It's a fine balance between preserving the unique characteristics of the coffee beans and bringing out their full potential through the right amount of time.
Different roasting techniques and their impact on flavour
While temperature and time are essential, the roasting technique employed can also have a significant impact on the flavour of the coffee. Two of the most common methods are drum roasting and air roasting.

Drum roasting is the traditional method, where the beans are roasted in a rotating drum. This technique allows for a longer contact time between the beans and the hot surfaces, resulting in a more even roast. Drum roasting tends to produce a fuller-bodied cup with well-developed flavours and aromas.
On the other hand, air roasting is a newer technique that involves suspending the beans in a stream of hot air. This method allows for faster and more precise control of the roasting process. Air roasting tends to result in a brighter, more acidic cup with distinct flavour characteristics.
Both techniques have their merits and can produce outstanding coffee. The choice of roasting technique often comes down to personal preference and the desired flavour profile. Some roasters even combine the two methods to create unique blends that showcase the best of both worlds.
The science behind the Maillard reaction in coffee roasting
The Maillard reaction is a crucial chemical process that occurs during coffee roasting and is responsible for the development of the complex flavours we associate with a well-roasted coffee. This reaction takes place between amino acids and reducing sugars, resulting in the formation of melanoidins – brown pigments that give coffee its characteristic colour.
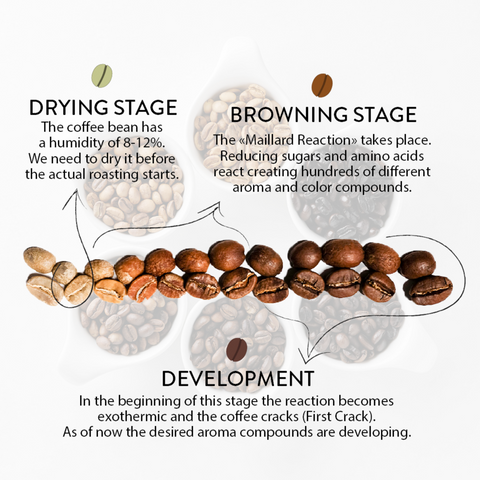
The Maillard reaction begins around 300°F (150°C) and continues until the beans reach their desired roast level. As the temperature increases, the amino acids and sugars react, forming a wide range of flavour compounds. These compounds contribute to the coffee's aroma, body, and taste.
The Maillard reaction is a delicate balance between heat and time. Too short a roast may result in underdeveloped flavours, while too long a roast can lead to burnt or bitter notes. Coffee roasters carefully monitor the progression of the Maillard reaction, adjusting the temperature and time as necessary to achieve the perfect balance of flavours.
Understanding the science behind the Maillard reaction allows coffee roasters to unlock the full potential of the beans and create the rich, complex flavours that coffee lovers crave.
Factors that affect coffee bean development during roasting
Several factors can influence the development of coffee beans during the roasting process. These factors include the origin of the beans, their moisture content, and the roasting environment.

The origin of the beans plays a significant role in determining their flavour profile. Different coffee-growing regions produce beans with distinct characteristics, such as acidity, body, and aroma. Roasters take these inherent qualities into account when developing their roast profiles, aiming to highlight the unique flavors of each origin.
The moisture content of the beans also affects the roasting process. Green coffee beans typically have a moisture content of around 10-12%. During roasting, this moisture evaporates, and the beans undergo physical and chemical changes. Roasters carefully monitor the moisture loss to ensure consistent results and avoid under or over development of the beans.
The roasting environment, including the airflow and humidity, can also impact the development of the beans. Proper airflow ensures even heat distribution, while humidity levels affect the drying phase of the roast. Roasters strive to create an optimal environment that allows for the desired flavor development while minimising any negative effects.
By understanding and manipulating these factors, coffee roasters can create unique roast profiles that showcase the best qualities of each bean and deliver a memorable coffee experience.
The art of cupping: evaluating coffee roast profiles
Cupping is a time-honored technique used by coffee professionals to evaluate and compare different roast profiles. It involves systematically tasting and analysing brewed coffee to assess its flavour, aroma, and other sensory attributes.
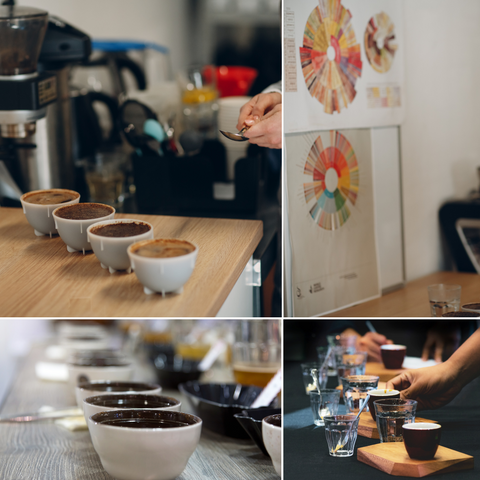

During a cupping session, coffee samples from different roasts or origins are prepared using standardised methods. The tasters then evaluate the coffees, noting their aroma, acidity, body, flavour, and aftertaste. This process allows roasters to objectively compare and assess the quality and characteristics of their coffees.
Cupping provides valuable feedback to coffee roasters, helping them refine their roast profiles and make adjustments to achieve the desired flavours. It's a skill that requires experience and a keen palate to identify subtle differences and nuances in the coffee. Through cupping, roasters can fine-tune their craft and consistently deliver exceptional coffee to their customers.
Common mistakes to avoid in coffee roasting
While coffee roasting is a blend of science and art, it's not without its challenges. Several common mistakes can affect the quality of the final product. Here are a few to watch out for:
1. Under or over-roasting:
Achieving the perfect roast level requires precise control of temperature and time. Under-roasting can result in a grassy or sour taste, while over-roasting can lead to burnt or bitter flavours.
2. Inconsistent heat distribution:
Uneven heat can cause some beans to roast faster than others, resulting in an inconsistent flavour profile. Proper airflow and agitation within the roasting drum are essential for even heat distribution.
3. Not paying attention to the roast curve:
The temperature profile or roast curve is a critical aspect of coffee roasting. Roasters need to carefully monitor and adjust the temperature throughout the roasting process to achieve the desired flavour development.
4. Neglecting the cooling process:
After roasting, the beans need to be rapidly cooled to stop the roasting process and preserve the flavours. Neglecting the cooling process can result in overdevelopment and loss of delicate flavours.
5. Storing roasted coffee improperly:
Roasted coffee is susceptible to oxidation and moisture absorption. Proper storage in airtight containers away from light and moisture is crucial to maintaining the coffee's freshness.
By avoiding these common mistakes and honing their skills, coffee roasters can consistently produce exceptional coffee that delights the senses.
Exploring specialty coffee roasters and their unique approaches
The world of specialty coffee is teeming with passionate roasters who take pride in their craft. Each specialty coffee roaster brings a unique approach to the art of coffee roasting, resulting in a diverse range of flavours and experiences for coffee enthusiasts.

Some roasters focus on single-origin coffees, carefully sourcing beans from specific regions and farms. They aim to highlight the unique characteristics of each origin, allowing coffee lovers to explore the nuances of different coffee-growing regions.
Others specialise in creating blends, combining beans from multiple origins to achieve a harmonious balance of flavours. These roasters artfully blend different beans, considering their individual characteristics and roast profiles to create a well-rounded and complex cup of coffee.
Specialty coffee roasters often prioritise sustainability and ethical sourcing practices. They work closely with farmers to ensure fair compensation and environmentally friendly farming methods. By supporting these roasters, coffee lovers can enjoy their favourite brew while making a positive impact on the coffee industry.
Exploring specialty coffee roasters and their unique approaches is a delightful journey that allows coffee enthusiasts to discover new flavours, support sustainable practices, and appreciate the artistry behind each cup.
Conclusion: unlocking the perfect cup through the science of coffee roasting
Coffee roasting is a captivating blend of science and art, where temperature, time, and technique come together to shape the flavors and aromas that we savor in our morning cup. The delicate dance of heat and time, guided by the roasting technique, unlocks the true potential of the coffee beans, creating a unique experience with every sip.
By understanding the importance of temperature and time in coffee roasting, we gain insight into the chemical reactions that occur within the beans and the development of their flavors. The science behind the Maillard reaction reveals the secrets behind the rich, complex taste that we crave.
Factors such as bean origin, moisture content, and the roasting environment further influence the coffee's development, adding depth and character to the final product. Through cupping, coffee roasters can evaluate and refine their roast profiles, ensuring consistent quality and flavor.
While coffee roasting is not without its challenges, avoiding common mistakes and embracing the unique approach of specialty coffee roasters can result in exceptional brews that delight the senses.
So, the next time you savor your morning cuppa, take a moment to appreciate the intricate science and artistry that went into creating that perfect blend. From temperature and time to the roasting technique, every step in the journey plays a crucial role in shaping the beloved beverage that kickstarts our day. Cheers to the science of coffee roasting and the joy it brings to our mornings!
